后台可以向前台发送Set-Cookie响应头,浏览器收到响应后会设置cookie,测试如下
app.js
const Koa = require('koa')
const app = new Koa()
app.use(async ctx => {
ctx.status = 200
ctx.set('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
ctx.set('Access-Control-Allow-Credentials', 'true');
ctx.set("WWW-Authenticate", `Basic realm="oauth2/client"`)
ctx.cookies.set(
'cid',
'hello world',
{
domain: 'http://localhost:5173', // 写cookie所在的域名
path: '/', // 写cookie所在的路径
maxAge: 10 * 60 * 1000, // cookie有效时长
expires: new Date('2017-02-15'), // cookie失效时间
httpOnly: false, // 是否只用于http请求中获取
overwrite: false // 是否允许重写
}
)
ctx.cookies.set('TestCookie2', 'Test12');
// ctx.cookies.set('jwt', token, { httpOnly: true, secure: true, sameSite: "none", secureProxy: true });
ctx.body = `hello world`
})
app.listen(3000)
首先测试get请求,浏览器直接输入url就是get请求
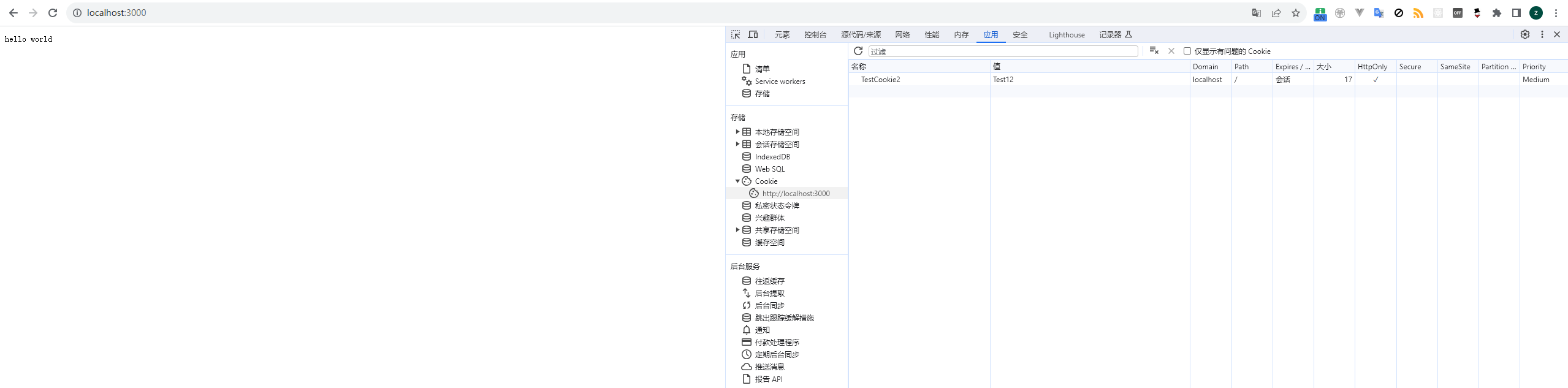
可以看到,再次刷新页面浏览器会自动将cookie放在请求头中发送到后台
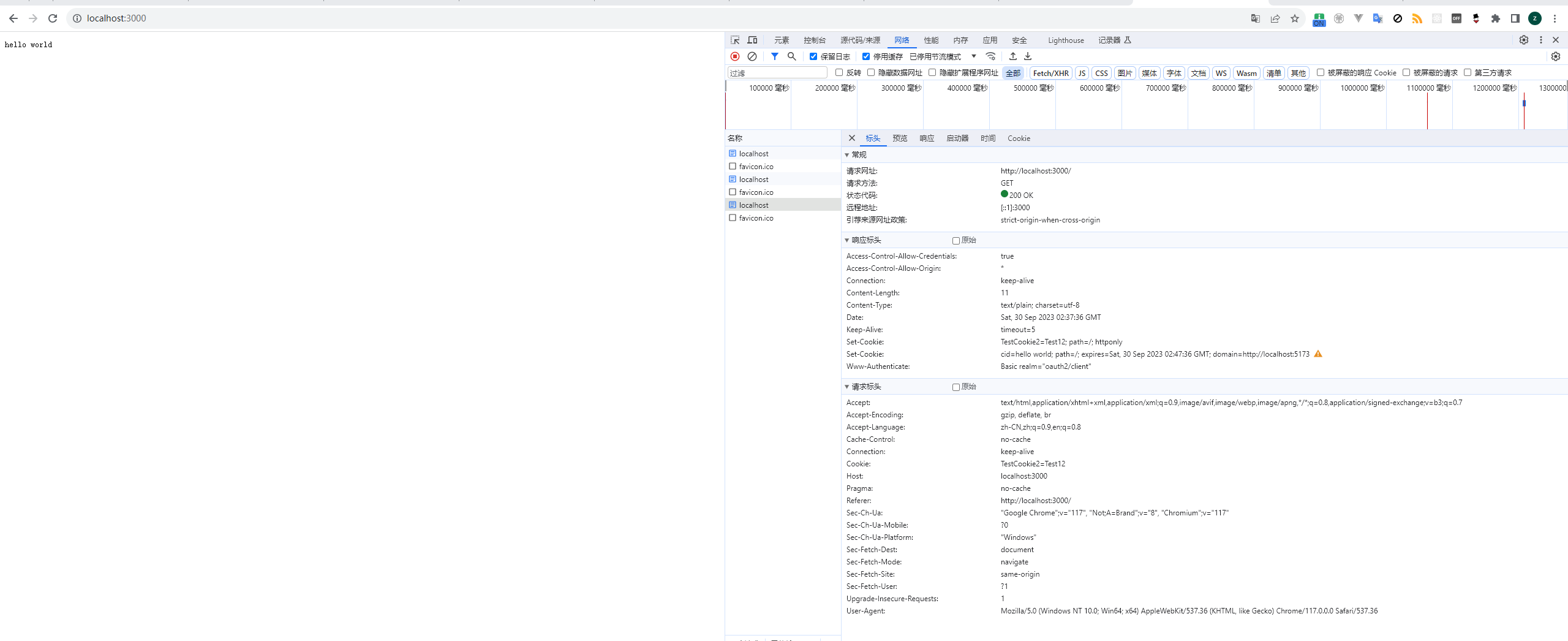
并且关闭浏览器后再次打开cookie也会保留
接下来测试post请求
post请求可以用浏览器原生的form标签来发送,代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://localhost:3000" method="post">
<div>
<label for="say">What greeting do you want to say?</label>
<input name="say" id="say" value="Hi" />
</div>
<div>
<label for="to">Who do you want to say it to?</label>
<input name="to" id="to" value="Mom" />
</div>
<div>
<button>Send my greetings</button>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
可以看到同样存储了cookie,但是会发现有两个问题:
- 点击按钮提交之后浏览器会刷新到localhost:3000的内容:即后台发送的hello world
- 再次发起post请求之后不会携带当前已经存储的cookie
针对方法一,可以使用网上的方法,iframe套一层
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://localhost:3000" method="post" target="frameName">
<div>
<label for="say">What greeting do you want to say?</label>
<input name="say" id="say" value="Hi" />
</div>
<div>
<label for="to">Who do you want to say it to?</label>
<input name="to" id="to" value="Mom" />
</div>
<div>
<button>Send my greetings</button>
</div>
</form>
<iframe src="" frameborder="0" name="frameName"></iframe>
</body>
</html>
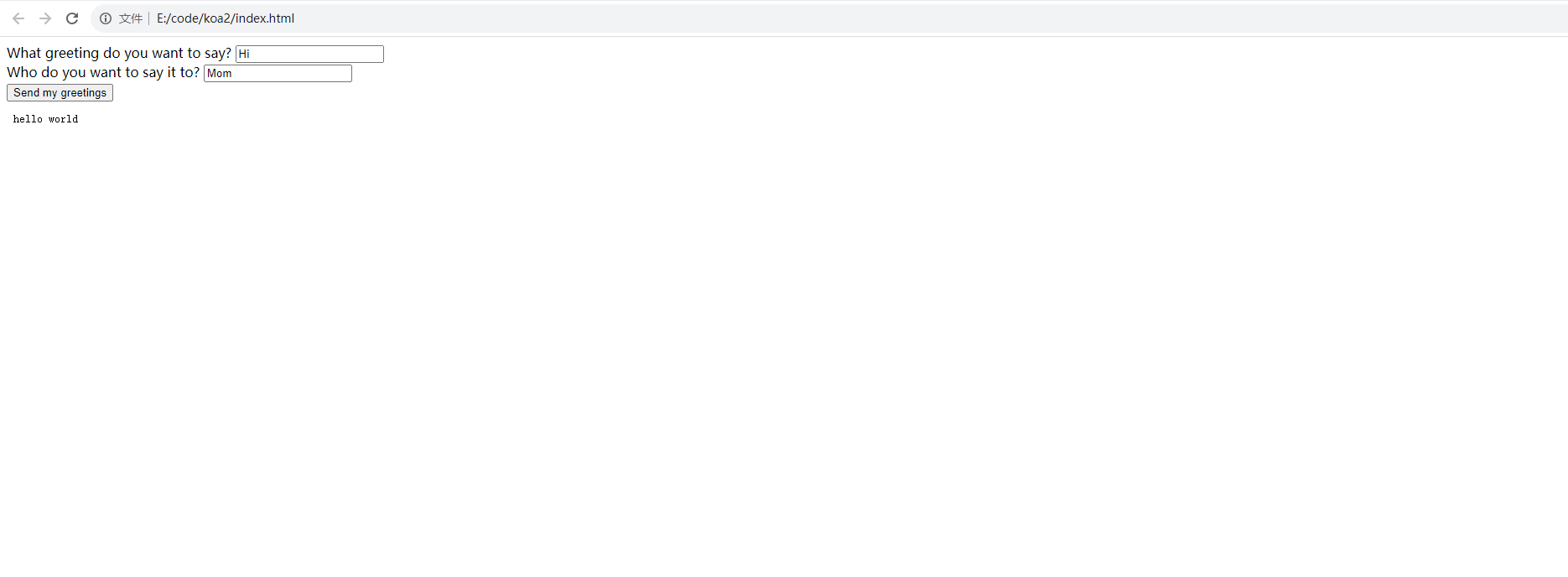
可以看到,现在点击提交之后结果如下:
针对问题二,应该是由于访问不在同一个域下的api,尝试一下直接在后台返回html测试一下
const Koa = require('koa')
const app = new Koa()
app.use(async ctx => {
ctx.status = 200
ctx.set('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
ctx.set('Access-Control-Allow-Credentials', 'true');
ctx.set("WWW-Authenticate", `Basic realm="oauth2/client"`)
ctx.cookies.set(
'cid',
'hello world',
{
domain: '*',
path: '/',
maxAge: 10 * 60 * 1000,
expires: new Date('2024-02-15'),
httpOnly: false,
overwrite: false
}
)
ctx.cookies.set('TestCookiePost', 'Test13');
if(ctx.url === '/' && ctx.method === 'GET') {
let html = `
<form action="/" method="post" target="frameName">
<div>
<label for="say">What greeting do you want to say?</label>
<input name="say" id="say" value="Hi" />
</div>
<div>
<label for="to">Who do you want to say it to?</label>
<input name="to" id="to" value="Mom" />
</div>
<div>
<button>Send my greetings</button>
</div>
</form>
<iframe src="" frameborder="0" name="frameName"></iframe>
`
ctx.body = html
}
})
app.listen(3000)
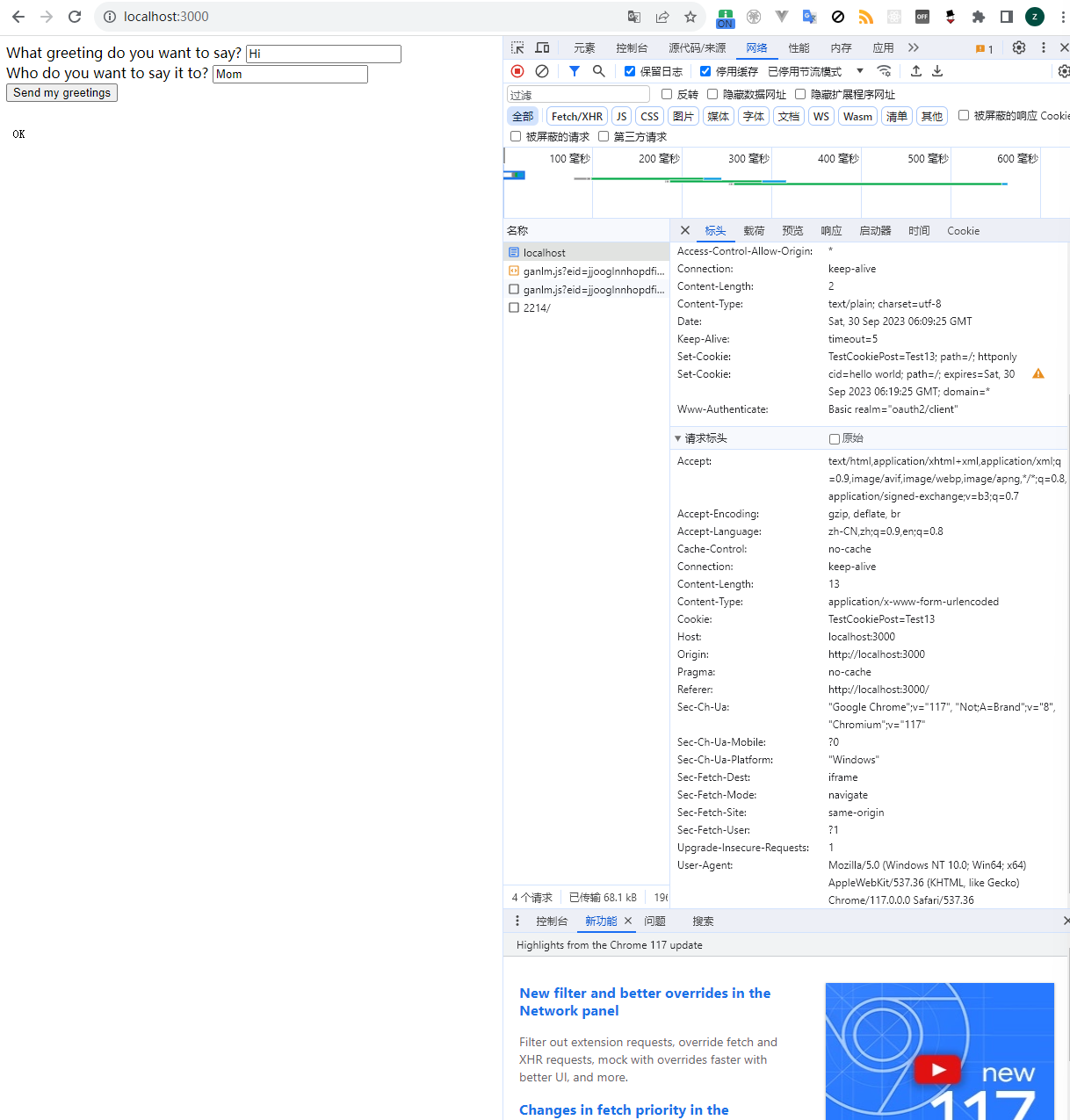
可以看到,这时候再次发送http请求就会带上cookie了
下面测试下ajax请求会不会默认携带cookie
使用Vite+Vue3简单搭建一个web项目,使用axios发送cookie,发现cookie既不会被写入,再次请求也不会携带cookie,使用nginx代理一下后台api,模拟一下生产环境,配置如下:
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:3000;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
这样的话,既能解决跨域问题,也能收到回写的cookie,并且在下次发送时可以携带cookie,下面解决在生产环境中的这个问题该怎么解决
既然本地已经起了nginx服务,那就让前台直接请求nginx的80端口,然后通过nginx转发,间接请求后台接口,现在问题是要解决前台端口和请求接口不一致的问题
在vite.config.js文件中配置代理,如下:
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [vue()],
server: {
proxy: {
"/api": {
target: "http://localhost:3000/",
changeOrigin: true,
},
},
},
})
可以看到,前端成功存储了后台发过来的cookie
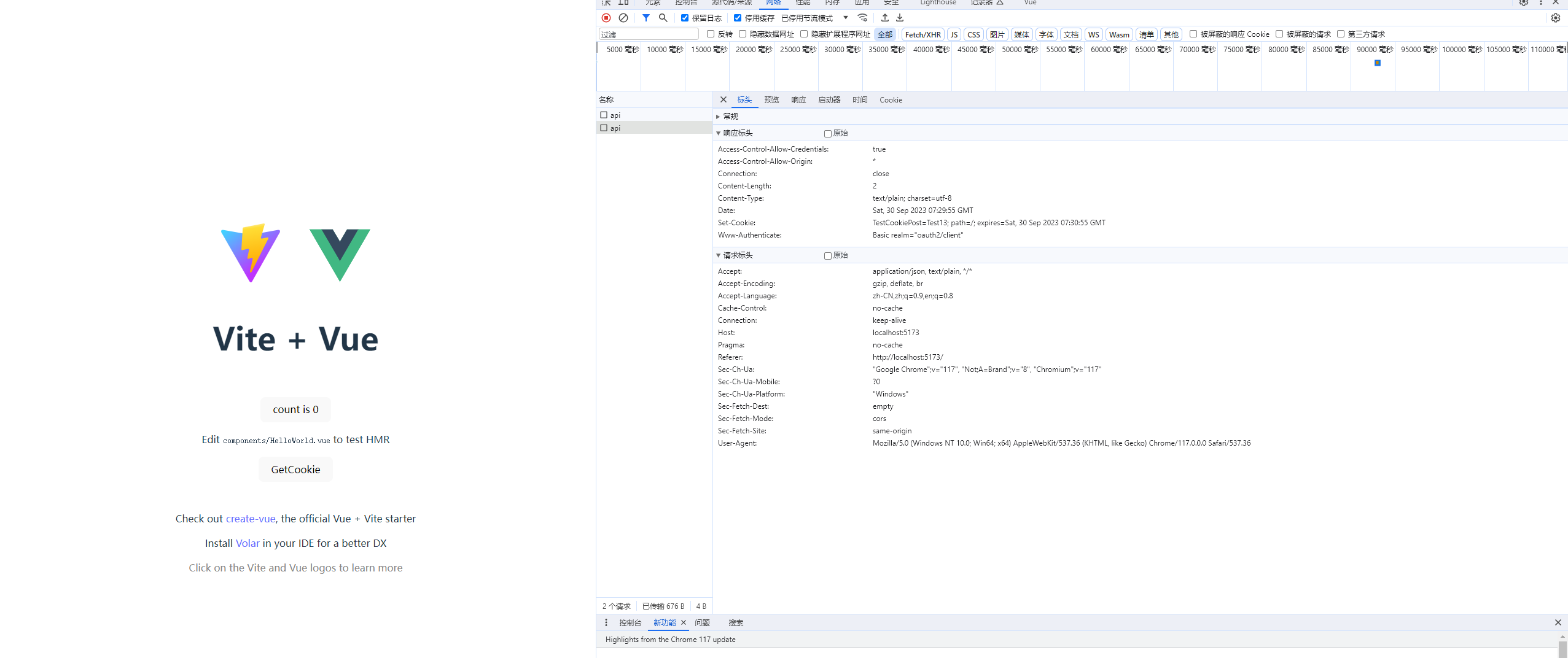
但是在再次发送请求中无法携带cookie,查阅资料知道,这种情况,可以通过设置axios的请求头解决
axios.get('/api', {
withCredentials: true
})
再次试验,发现再次请求是会携带cookie的。
到此为止,可以得出结论,由于浏览器的限制,cookie的设置和携带需要客户端和服务端的配置,客户端和服务端都可以操作cookie,在请求时最好不要将api的域写死,方便在开发和生产环境切换,比如写/api,这样即使nginx和http-server的端口不一致,也只需要改动各自的配置文件即可正常运行。